Conservation of Energy
Conservation of Energy: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Mechanical Energy, Dissipation of Energy, Speed Management, Conservation of Energy in Free Fall, Cause behind Dissipation of Mechanical Energy, Stopping Distance of a Toy and, Fraction of Energy Lost by a Bouncy Ball
Important Questions on Conservation of Energy
Vyom drop a gram ball from a height of and ball bounce upon calculate energy lost by ball.
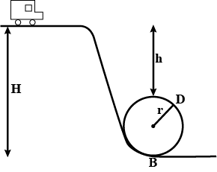
A toy car rolls down the inclined plane as shown in the above figure. It loops at the bottom. What is the relation between H and h?
Dissipation of energy happens when energy is converted from one form to another.
Mechanical energy is dissipated due to friction.
Describe the rules which should be followed by pedestrians while walking or crossing a road.
Is the kinetic energy of a vehicle and the impacts caused by the accident due to that vehicle connected? Explain
A toy car on a slide is travelling at . Child puts on the brakes when he wants to stop the car. The coefficient of friction between the tires and the slide is . What is the stopping distance of the car?
A toy car is travelling at . Child puts on the brakes when he wants to stop. The coefficient of friction between the tires and the floor is . What is the stopping distance of the car?
Total energy of an isolated system-
A ball is thrown vertically up with a velocity . At what height will its kinetic energy be half its original value?
An object is dropped from a certain distance when she is at half distance she is ______ in it?
A toy car has a kinetic energy of . It rolls up a slope and at the top it has of gravitational potential energy and of kinetic energy. How much energy has the car lost through friction?
An aeroplane flying at a height of has _____.
When a body falls freely towards the earth, then its total energy
The energy possessed by an aeroplane flying at an altitude is
From a building two balls to are thrown such that is thrown upwards and downwards (both vertically). If and are their respective velocities on reaching the ground, then
